Data breaches are one of the worst issues your business may encounter. Cybercriminals can leak your confidential information to the public, or use it for their personal, professional, and financial gain.
Enterprises and small businesses alike have been affected by data leaks. While a data breach happens in less than one minute, it takes an average of 206 days for companies to detect the issue, and another 73 to recover.
As a result, businesses suffer the following repercussions:
#1. Reputational damage
One of the biggest data breach consequences is reputational damage. Your customers trust you to keep their information safe from prying eyes. But if their names, email addresses, credit card numbers, home addresses, and other personal information are leaked, potential leads will hesitate to do business with you.
Facebook is a prime example of this. After the 2018 Cambridge Analytica scandal, people lost trust in the social media company, which led to many deleting their accounts. The same fate that befell a large enterprise like Facebook can also happen to a small business.
#2. Financial loss
Following a data breach, customers will hesitate to spend on your services, leading to a larger revenue loss. Your business will also have to bear the costs of containing the breach, compensating affected clients, and investing in security solutions.
Many organizations are also slapped with regulatory fines for violating data compliance laws. For instance, the penalties under the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) range from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum fine of $1.5 million per year. Some violations can also result in imprisonment.
Overall, the global average cost of a data breach is $3.9 million, enough to put many companies out of business.
FREE tool: Do you know how much a data breach could cost you? Calculate now.
#3. Operational disruptions
Depending on the severity, data breaches can affect your company’s operations. To illustrate, your company will need to keep the problem under control and inform affected customers. Subsequent investigations and recovery processes can also hamper the normal operations of your organization.
While large enterprises have deep pockets to weather operational disruptions, the story isn’t the same for small- to medium-sized businesses (SMBs). Studies have shown that 60% of SMBs that suffered a data breach go out of business within six months.
#4. Online vandalism
Data breaches may encourage pranksters to defame your website and social media accounts. For instance, your Facebook page can get spammed with threatening or nonsensical messages. Others may modify the contents of your website or write vulgar content. Cybercriminals may also inject malware into your website, which can harm visitors.
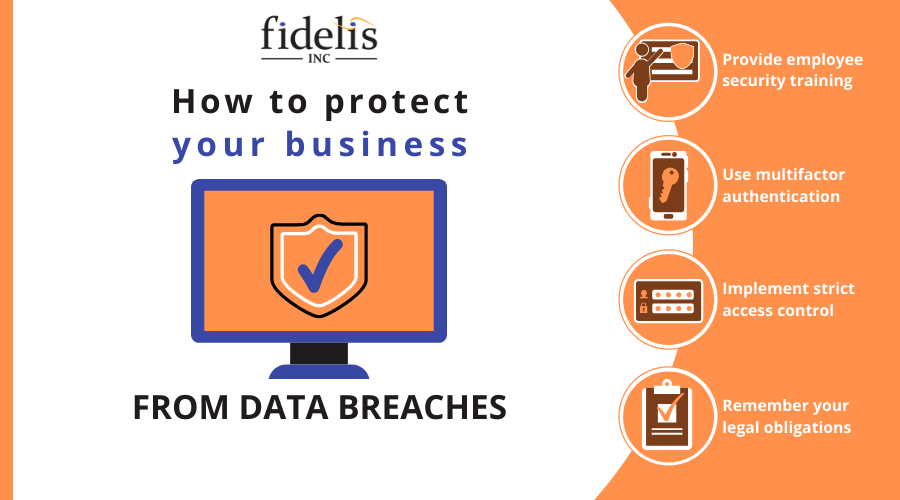
How to protect your business from data breaches
No business is safe from data breaches as cybercriminals devise more sophisticated methods to steal sensitive information. But organizations can stay proactive by following these tips:
#1. Provide employee security training
Conduct simulated phishing exercises to help your employees identify online scams. Teach your staff as well to use strong passwords and avoid opening potentially malicious files.
#2. Use multifactor authentication (MFA)
MFA acts as a secondary security method on top of passwords. This could be a one-time SMS code, smartphone prompt, facial recognition, or fingerprint. Even if a cybercriminal acquires a user’s login details, they won’t be able to access the account without fulfilling the subsequent authentication methods.
#3. Implement strict access control
Your business’s data must be accessible only to authorized users. You can use access management software like Microsoft Azure to ensure employees only access the data they need.
Looking for a reliable security solution?
Still unsure how to secure your business? Read our eBook, 3 Essential types of cyber security solutions your business must have and find out how you can optimize your business's cybersecurity without spending too much.
#4. Remember your legal obligations
Your business must be compliant with applicable industry privacy laws. For instance, under the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), you are required to protect the information of EU citizens. Meanwhile, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) mandates companies to protect the privacy of California residents.
Your business should be proactive against data breaches. Fidelis offers state-of-the-art managed IT solutions that will protect you from all known threats so you can focus more on important business matters. Download our FREE managed services eBook today to learn how we can help your Seattle or Oregon business.